Introduction
Symbolic Regression is a type of regression analysis that searches the space of mathematical expressions to find the model that best fits a given dataset, both in terms of accuracy and simplicity. While conventional regression techniques seek to optimize the parameters for a pre-specified model structure, symbolic regression avoids imposing prior assumptions, and instead infers the model from the data. Common representation of the SR model is an expression tree.
- An example of the expression tree for $x^3+x^2+x$
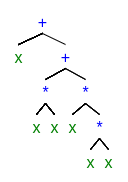
Genetic Programming (GP) evolves computer programs, traditionally represented as expression tree structures. Some of the applications of GP are curve fitting, data modeling, symbolic regression, feature selection, classification, etc.
Benchmark Function
We begin by importing some Julia libraries
using Evolutionary
using Random
using Plots
Plots.gr()
default(fmt = :png)
┌ Info: Precompiling Evolutionary [86b6b26d-c046-49b6-aa0b-5f0f74682bd6]
└ @ Base loading.jl:1273
We need to generate some data from Nguyen-1 benchmark function: $x^3+x^2+x$
Random.seed!(42);
d, n = 1, 20
Nguyen1(x) = x*x*x + x*x + x
xs = sort!(2*rand(n).-1)
20-element Array{Float64,1}:
-0.9646263465700713
-0.6799878057158164
-0.6541339421260974
-0.6461828007342891
-0.4743823295397043
-0.3922607778264351
-0.27308315609588885
-0.2330176105940942
-0.1540874689837164
-0.09194172882571516
0.00590422275549729
0.06636603208772263
0.16856829512576077
0.18582314647694176
0.20459516053276605
0.49036263858165396
0.8749326091650076
0.9138316481785176
0.9178517526594696
0.9471319596073715
Next, we define collection of symbols and operations used for construction of of the genetic program expression.
First, we define the symbols
syms = [:x]
1-element Array{Symbol,1}:
:x
and, the allowed functions
funcs = Function[+, -, *, /]
4-element Array{Function,1}:
+
-
*
/
Let’s define the fitness function for evaluation of the genetic program as root-mean-square error (RMSE)
fitobj(expr) = sum( abs2.(Nguyen1.(xs) - Evolutionary.Expression(expr).(xs)) )/length(xs) |> sqrt
fitobj (generic function with 1 method)
Test some arbitrary expression with our fitness function
expr = Expr(:call, *, :x, :x)
println("Evaluate expression: ", Evolutionary.Expression(expr).(xs))
println("Obj. func = ", fitobj(expr))
Evaluate expression: [0.9305039884971232, 0.4623834159222109, 0.42789121424142856, 0.41755221196481, 0.22503859457951658, 0.15386851782099986, 0.0745744101432916, 0.054297206846980924, 0.02374294809780776, 0.008453281499461342, 3.4859846346532014e-5, 0.004404450215068629, 0.028415270121605583, 0.034530241766590954, 0.04185917971342831, 0.2404555173167618, 0.7655070705802879, 0.835088281212666, 0.8424518398600602, 0.8970589489096996]
Obj. func = 0.9660246588120451
Now, we use TreeGP optimization algorithm that will construct a symbolic solution for
Random.seed!(987498737423);
res = Evolutionary.optimize(fitobj,
TreeGP(50, Terminal[syms...], funcs,
mindepth=1,
maxdepth=4,
optimizer = GA(
selection = uniformranking(5),
ɛ = 0.1,
mutationRate = 0.95,
crossoverRate = 0.05,
),
)
)
* Status: success
* Candidate solution
Minimizer: (+)((*)(x, (+)((*)(x, x), x)), x)
Minimum: 3.5652682413747996e-17
Iterations: 20
* Found with
Algorithm: TreeGP[P=50,Parameter[x],Function[*, +, /, -]]
We can generate minimizing expression in LaTeX format
Evolutionary.minimizer(res) |> Evolutionary.Expression
((x*((x*x)+x))+x)
The minimizing expression $$\left(\left(x*\left(\left(x*x\right)+x\right)\right)+x\right)$$
Symbolic Regression
Linear
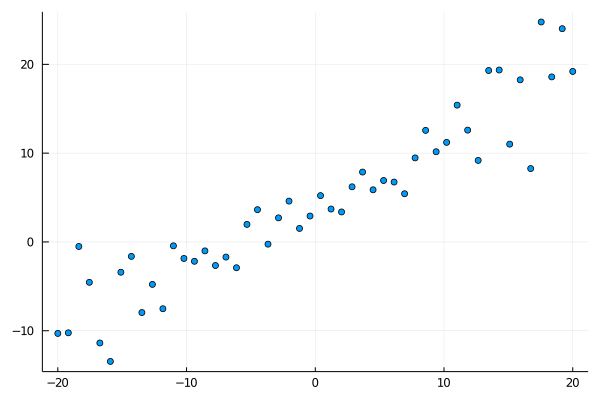
We generate a dataset to work with
Random.seed!(42);
n = 50
xs = range(-20, 20, length=n) |> collect
ys = (rand(n).*0.8.+0.3).*xs + (rand(n).*5.0.+2.0)
xs, ys
([-20.0, -19.183673469387756, -18.367346938775512, -17.551020408163264, -16.73469387755102, -15.918367346938776, -15.10204081632653, -14.285714285714286, -13.46938775510204, -12.653061224489797 … 12.653061224489797, 13.46938775510204, 14.285714285714286, 15.10204081632653, 15.918367346938776, 16.73469387755102, 17.551020408163264, 18.367346938775512, 19.183673469387756, 20.0], [-10.301775957695707, -10.233893692226244, -0.5108186849245042, -4.548650362389421, -11.37884481662021, -13.45714316027289, -3.411883269164912, -1.6257189913947885, -7.9511271443853495, -4.779000246208424 … 9.182787509211524, 19.30856201963916, 19.363218214500648, 11.01307966019218, 18.25693527098487, 8.264341990912298, 24.771086256895913, 18.58907728951158, 24.017965869842424, 19.200868554184602])
scatter(xs, ys, leg=:none)
Define our objective function and test it with an arbitrary exression
fitobj(expr) = sum( abs2.(ys - Evolutionary.Expression(expr).(xs)) ) |> sqrt
expr = Expr(:call, *, :x, :x)
println("Obj. func = ", fitobj(expr))
Obj. func = 1290.672514731313
We need to the symbol collection rand function which will alow to generate numerical constanst in addition to the symbolical variables. For each symbol we specify its arity.
syms = Dict(:x=>1, (rand) => 1)
Dict{Any,Int64} with 2 entries:
rand => 1
:x => 1
We define linear operations, and provide their arity.
funcs = Dict((+) => 2, (-) => 2, (*) => 2, (/) => 2)
Dict{Function,Int64} with 4 entries:
* => 2
+ => 2
/ => 2
- => 2
We also need to increase maximum depth for the expression tree to accommodate more complex expressions
Random.seed!(987498737423);
res = Evolutionary.optimize(fitobj,
TreeGP(
populationSize = 500,
terminals = syms,
functions = funcs,
mindepth=1,
maxdepth=3,
initialization=:full,
optimizer = GA(
selection = uniformranking(2),
mutationRate = 0.1,
crossoverRate = 0.95,
ɛ = 0.001
),
),
Evolutionary.Options(iterations=50, show_trace=true, show_every=10)
)
Iter Function value
0 0.0
* time: 0.016000986099243164
10 23.070150702286064
* time: 0.5699429512023926
20 23.050119363563365
* time: 0.8840680122375488
* Status: success
* Candidate solution
Minimizer: (-)((+)((/)(0.7443415808289588, 0.2519046833943326), (*)(x, 0.7443415808289588)), (-)((-)(x, 0.7443415808289588), (+)(x, 0.7443415808289588)))
Minimum: 23.050119363563365
Iterations: 29
* Found with
Algorithm: TreeGP[P=500,Parameter[x],Function[*, +, /, -]]
Here is our minimizing expression
ex = Evolutionary.Expression(Evolutionary.minimizer(res))
(((0.744/0.252)+(x*0.744))-((x-0.744)-(x+0.744)))
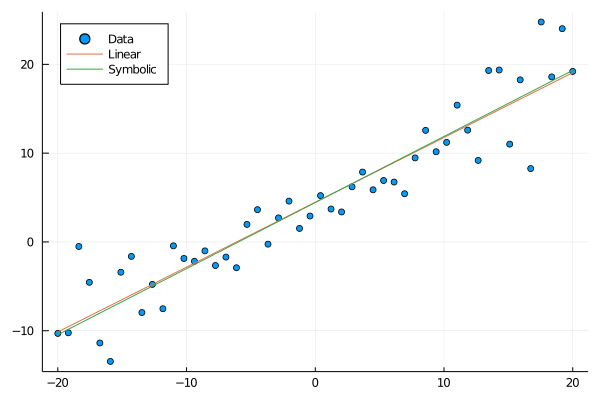
Calculate least squares solution for comparison
X = hcat(ones(n), xs)
β = inv(X'X)*X'ys
2-element Array{Float64,1}:
4.467274179301777
0.7300600401251902
scatter(xs, ys, label="Data", legend=:topleft)
plot!(xs, β[2].*(xs).+β[1], label="Linear")
plot!(xs, ex.(xs), label="Symbolic")
Nonlinear
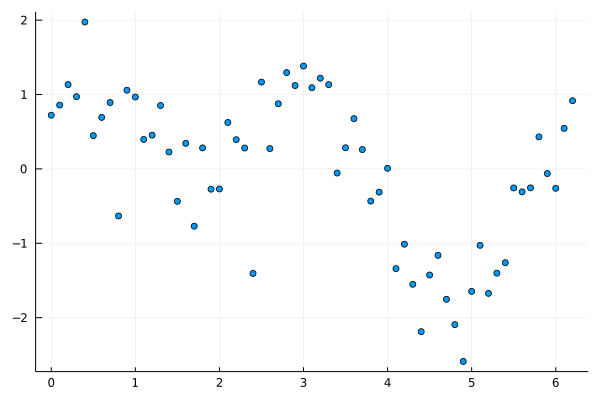
Now, let’s generate some noisy with nonlinear data
Random.seed!(42);
xs = collect(0:0.1:2*pi) |> sort!
ys = sin.(xs) + cos.(xs + xs) .+ randn(length(xs))./2
xs, ys
([0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.30000000000000004, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6000000000000001, 0.7000000000000001, 0.8, 0.9 … 5.300000000000001, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6000000000000005, 5.7, 5.800000000000001, 5.9, 6.0, 6.1000000000000005, 6.2], [0.7219865619268069, 0.8577083159332218, 1.1333079938025434, 0.9711137763915625, 1.9750556006844782, 0.44727707860793275, 0.6926972867878716, 0.8922565614583021, -0.6328389354401641, 1.0577797656641383 … -1.4019731481680853, -1.2610491311786165, -0.25605035540673443, -0.3085504793933047, -0.2547580599017927, 0.43075074590266565, -0.06247315632300754, -0.2608450734190263, 0.5449753531328724, 0.9167487102317231])
scatter(xs, ys, leg=:none)
We also expend the function collection with sin, cos, log, and exp. We also provide arity for each function.
funcs = Dict((+) => 2, (-) => 2, (*) => 2, (/) => 2,
(sin) => 1, (cos) => 1)
#(^)=>2, (log) => 1, (exp) => 1)
Dict{Function,Int64} with 6 entries:
* => 2
+ => 2
sin => 1
/ => 2
- => 2
cos => 1
We also need to increase maximum depth for the expression tree to accommodate more complex expressions
Random.seed!(9874987374243);
res = Evolutionary.optimize(fitobj,
TreeGP(
populationSize = 1000,
terminals = syms,
functions = funcs,
mindepth=1,
maxdepth=4,
initialization=:grow,
optimizer = GA(
selection = uniformranking(5),
mutationRate = 0.1,
crossoverRate = 0.8,
ɛ = 0.001
),
),
Evolutionary.Options(iterations=60, show_trace=true, show_every=15)
)
Iter Function value
0 0.0
* time: 0.00010800361633300781
15 4.072232948324664
* time: 0.41045403480529785
* Status: success
* Candidate solution
Minimizer: (+)((cos)((+)(x, x)), (sin)((sin)(x)))
Minimum: 4.072232948324664
Iterations: 16
* Found with
Algorithm: TreeGP[P=1000,Parameter[x],Function[*, +, sin, /, -, cos]]
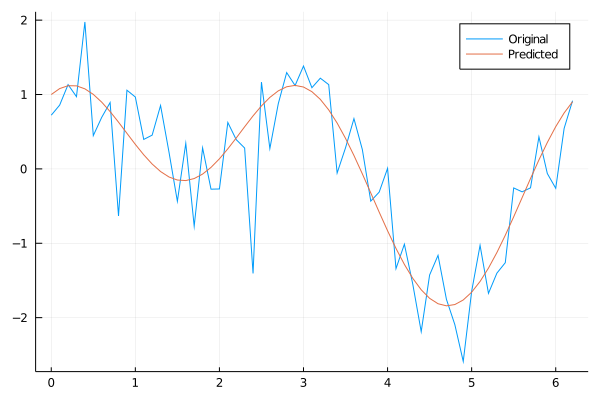
Here is the resulting expression, and the plot of this expression evaluated on the original data.
- The resulting expression is very close to the original data-generating function, $\sin(x) + \cos(x + x) + \varepsilon$.
ex = Evolutionary.Expression(Evolutionary.minimizer(res) |> copy)
(cos((x+x))+sin(sin(x)))
plot(xs, ys, label="Original")
plot!(xs, ex.(xs), label="Predicted")
Expression Simplification
However, sometimes, the generated expression can be quite long
Random.seed!(987498737424);
res = Evolutionary.optimize(fitobj,
TreeGP(
populationSize = 500,
terminals = syms,
functions = funcs,
mindepth=1,
maxdepth=5,
initialization=:grow,
optimizer = GA(
selection = uniformranking(2),
mutationRate = 0.15,
crossoverRate = 0.8,
ɛ = 0.001
),
),
Evolutionary.Options(iterations=50, show_trace=true, show_every=15)
)
Iter Function value
0 0.0
* time: 9.202957153320312e-5
15 4.928502370610355
* time: 0.717289924621582
30 4.7741079939719295
* time: 2.1325550079345703
* Status: success
* Candidate solution
Minimizer: (cos)((-)((+)((*)((-)((+)((*)((*)((-)((+)((+)((*)((-)((+)((*)((*)((-)((+)((*)((*)((-)(0.9450845364794724, x), 0.9450845364794724), 0.9450845364794724), (cos)(0.9450845364794724)), 0.9450845364794724), 0.9450845364794724), 0.9450845364794724), (cos)(0.9450845364794724)), 0.9450845364794724), (sin)(x)), (cos)(0.9450845364794724)), (cos)(0.9450845364794724)), 0.9450845364794724), 0.9450845364794724), 0.9450845364794724), (cos)(0.9450845364794724)), 0.9450845364794724), (sin)(x)), (cos)(0.9450845364794724)), 0.9450845364794724))
Minimum: 4.7741079939719295
Iterations: 41
* Found with
Algorithm: TreeGP[P=500,Parameter[x],Function[*, +, sin, /, -, cos]]
The minimizer function is quite long, so we might want to simplify it. We’ll use SymPy package functionality to perform the expression simplification.
using SymPy, PyCall
sympycore = pyimport("sympy.core")
# Convert sympy expression back to the julia expression
function convert(::Type{Expr}, sexpr::Sym)
# deal with numbers and symbols
if sexpr.is_Float
return Float64(sexpr.num)
elseif sexpr.is_Rational
return Float64(sexpr.evalf().num)
elseif sexpr.is_Symbol
return Symbol(sexpr.name)
end
# convert functions
expr = Expr(:call)
fn, (le, re) = if sexpr.is_Function
fname = Symbol("$(sexpr.func)"[10:end])
a2 = length(sexpr.args) > 1 ? sexpr.args[2] : nothing
eval(fname), (sexpr.args[1], a2)
elseif sexpr.func == sympycore.mul.Mul
(*), sexpr.as_two_terms()
elseif sexpr.func == sympycore.power.Pow
(^), sexpr.args[1:2]
elseif sexpr.func == sympycore.add.Add
(+), sexpr.as_two_terms()
end
# println(fn, " ", le, " ", re)
push!(expr.args, fn)
push!(expr.args, convert(Expr, le))
re !== nothing && push!(expr.args, convert(Expr, re))
return expr
end
function simplify!(ex::Expr)
expr = Evolutionary.Expression(ex)
length(expr.syms) == 0 && return ex
sexpr = eval(Expr(:call, expr, map(Sym ∘ string, expr.syms)...))
sexpr = SymPy.simplify(sexpr)
copyto!(ex, convert(Expr, sexpr))
end
simplify! (generic function with 1 method)
ex = simplify!(Evolutionary.minimizer(res)) |> Evolutionary.Expression
cos((0.359+((0.157+((-0.066+(0.713*x))*sin(x)))*sin(x))))
We can generate a LaTeX expression of the simplified minimizer
display("text/latex", ex)
\cos\left(\left(0.359+\left(\left(0.157+\left(\left(-0.066+\left(0.713x\right)\right)\sin\left(x\right)\right)\right)*\sin\left(x\right)\right)\right)\right)
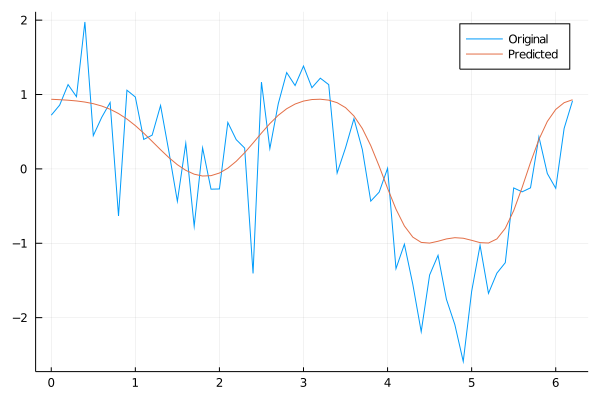
Thus, the simplified expression is the following:
$$cos\left(\left(0.359+\left(\left(0.157+\left(\left(-0.066+\left(0.713*x\right)\right)*sin\left(x\right)\right)\right)*sin\left(x\right)\right)\right)\right)$$
We can plot resulting function along with original data
plot(xs, ys, label="Original")
plot!(xs, ex.(xs), label="Predicted")
You can find the corresponding Jupyter notebook in the Evolutionary package repository.